Piercing Anatomy: A Deep Dive into the Science Behind Body Piercings
- AmazoniaSilva
- Tháng 12 26, 2024
- Zodiac signs
- 0 Comments
Piercing Anatomy is a critical aspect to consider before getting any piercing. Understanding the underlying structures of your skin, muscles, and cartilage can help ensure a safe, healthy, and aesthetically pleasing piercing. This comprehensive guide will explore the various aspects of piercing anatomy, providing you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your next piercing.
Understanding Skin Layers and Piercing
The skin, our body’s largest organ, plays a crucial role in the healing process of a piercing. A piercing essentially creates a controlled wound that your body then heals around the jewelry. Knowing the three main layers – epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis – is fundamental to understanding piercing anatomy. The epidermis is the outermost layer, acting as a protective barrier. The dermis contains blood vessels, nerves, and hair follicles. The hypodermis, the deepest layer, consists primarily of fat and connective tissue. Different piercings interact with these layers in various ways, influencing healing time and potential complications. For instance, a surface piercing sits within the dermis and epidermis, making it more prone to rejection if not placed correctly.
Cartilage Piercings: A Closer Look at Anatomy
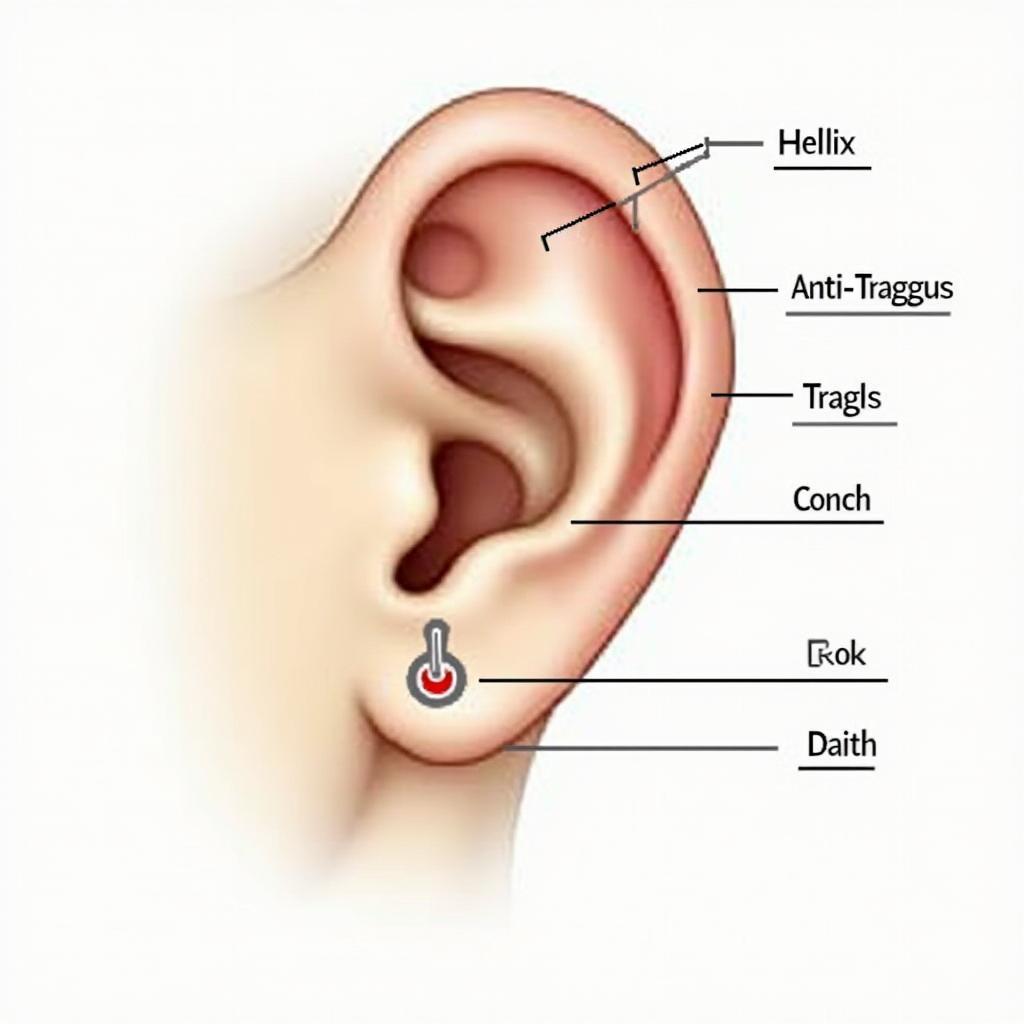
Cartilage piercings, popular choices like helix, tragus, and conch piercings, involve puncturing the flexible connective tissue that shapes our ears and nose. Cartilage is avascular, meaning it doesn’t have a direct blood supply, which results in longer healing times compared to piercings through fleshy areas. Understanding the specific cartilage anatomy of the area being pierced is crucial for avoiding complications and ensuring proper jewelry placement. For example, a constellation ear piercing requires careful consideration of the ear’s cartilage structure to create a balanced and aesthetically pleasing arrangement.
 Anatomy of Ear Cartilage for Piercings
Anatomy of Ear Cartilage for Piercings
Piercing Placement and Nerve Pathways
Nerves are another vital element of piercing anatomy. While piercing inevitably involves some level of discomfort, proper placement is crucial to minimize pain and avoid nerve damage. A skilled piercer understands the intricate network of nerves throughout the body and carefully selects piercing locations to avoid major nerve pathways. This knowledge is especially important for facial piercings or those in sensitive areas.
Muscles and Piercings: Understanding Movement and Healing
Muscles also play a role in piercing anatomy, particularly in areas with significant movement, such as the tongue or eyebrow. Placement needs to account for muscle contractions and potential impact on jewelry stability and healing. An improperly placed tongue piercing, for example, could interfere with speech or chewing.
Choosing the Right Jewelry: Material and Anatomy
Selecting the right jewelry material is crucial for a healthy piercing. Implant-grade titanium and gold are often recommended for their biocompatibility and reduced risk of allergic reactions. The jewelry’s size and shape should also complement the pierced area’s anatomy. For example, a non piercing clit jewelry provides a way to explore adornment without the commitment of a traditional piercing.
Aftercare and Healing: Supporting Your Body’s Natural Processes
Proper aftercare is essential for a healthy healed piercing. Cleaning the piercing regularly with a saline solution helps prevent infection. Avoiding touching or rotating the jewelry minimizes irritation and promotes healing. Understanding piercing anatomy and the body’s natural healing processes helps you make informed decisions about aftercare.
Conclusion: Piercing Anatomy – Your Guide to Safe and Beautiful Body Art
Piercing anatomy is a fascinating and crucial subject for anyone considering a piercing. Understanding the underlying structures of your body, including skin, cartilage, nerves, and muscles, empowers you to make informed choices about piercing placement, jewelry selection, and aftercare. This knowledge ensures a safer, healthier, and more aesthetically pleasing piercing experience. Exploring options like chain ear piercings or ear piercing art can further enhance your understanding of piercing aesthetics and possibilities. Remember, knowledge is key to making the best decisions for your body.
FAQ
- What is the most important aspect of piercing anatomy to consider? Understanding the location of nerves and blood vessels is crucial for minimizing pain and avoiding complications.
- Why do cartilage piercings take longer to heal? Cartilage lacks a direct blood supply, resulting in a slower healing process compared to fleshy areas.
- What type of jewelry is best for initial piercings? Implant-grade titanium and gold are often recommended for their biocompatibility.
- How can I find a reputable piercer with a good understanding of anatomy? Research and choose a piercer with experience, proper certifications, and a focus on safe practices.
- What are the signs of a piercing infection? Redness, swelling, excessive pain, and discharge are common signs of infection.
- How long does a typical earlobe piercing take to heal? Earlobe piercings typically heal within 6-8 weeks.
- Can I change my piercing jewelry myself during the healing process? It’s generally recommended to avoid changing jewelry until the piercing is fully healed.
Common Piercing Situations and Questions
- Pain Sensitivity: Individuals have different pain thresholds. Discuss your concerns with your piercer to choose a location and technique that minimizes discomfort.
- Allergic Reactions: If you have metal sensitivities, opt for hypoallergenic materials like titanium or gold.
- Healing Challenges: Some piercings may be more prone to complications. Research and discuss potential risks with your piercer.
Further Exploration
You might also be interested in learning more about extreme labia piercing.
Need Help?
Contact us at [email protected] or visit us at Fifth Avenue, 34th Floor, New York, NY 10118, USA. Our customer support team is available 24/7.


