Breast Implant Under Fascia: A Comprehensive Guide
- AmazoniaSilva
- Tháng 1 5, 2025
- Zodiac signs
- 0 Comments
Breast Implant Under Fascia, also known as subfascial breast augmentation, is a surgical technique where the implant is placed beneath the pectoral fascia, the thin layer of tissue covering the chest muscle. This approach offers a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages compared to the more common subglandular placement. This article will delve into the intricacies of this procedure, exploring its benefits, risks, recovery process, and ideal candidates.
Understanding Breast Implant Under Fascia Placement
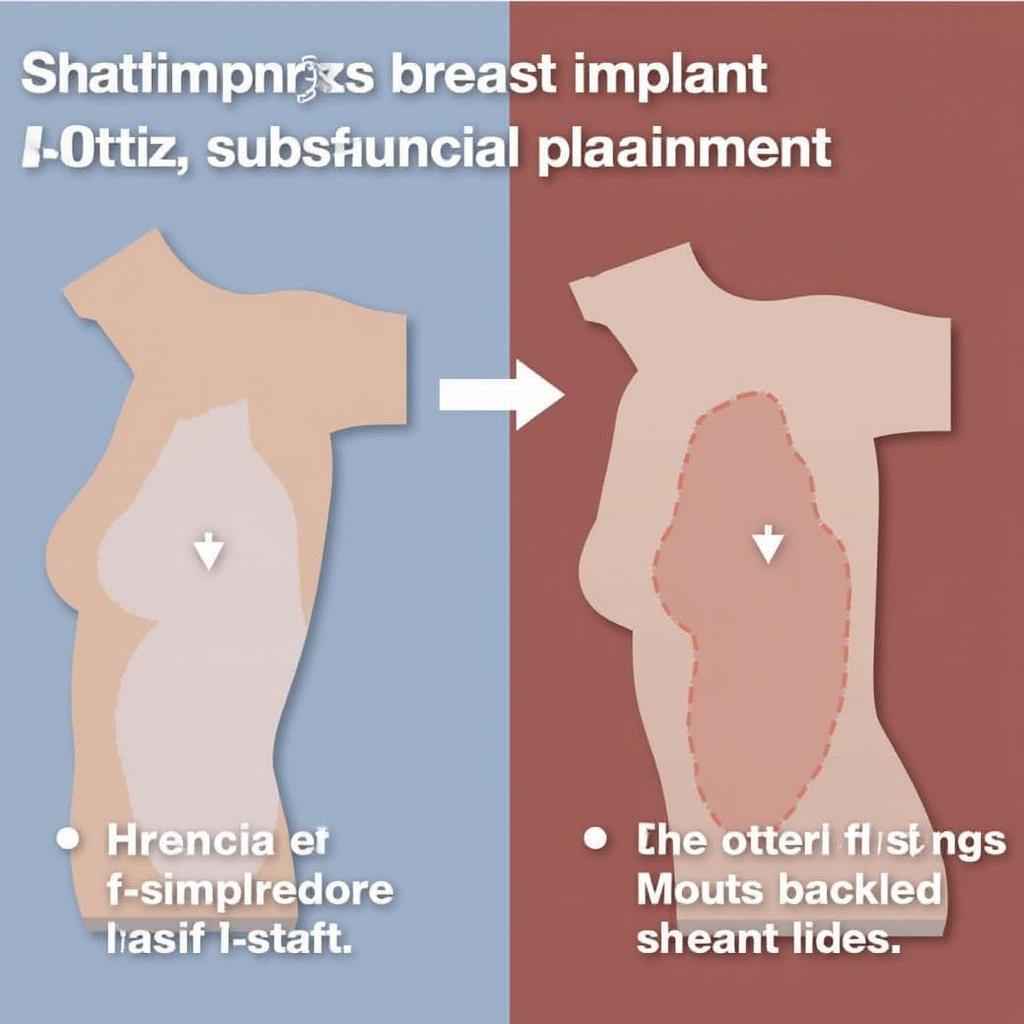
Subfascial placement involves positioning the breast implant partially beneath the pectoral muscle and partially beneath the fascia. This technique offers several potential benefits, including a more natural look and feel, especially in women with thinner breast tissue. It can also offer added coverage and support for the implant, potentially reducing the risk of certain complications like rippling and capsular contracture.
Benefits of Subfascial Breast Augmentation
Choosing the subfascial technique can offer several advantages:
- Reduced Rippling: The pectoral fascia provides an extra layer of coverage, minimizing the visibility of implant edges, especially in women with minimal breast tissue.
- Natural Look and Feel: By positioning the implant partially under the muscle, a more natural slope and shape can be achieved, mimicking the appearance of natural breast tissue.
- Lower Risk of Capsular Contracture: Some studies suggest that subfascial placement may reduce the risk of capsular contracture, a complication where scar tissue around the implant tightens, causing discomfort and distortion.
- Better Upper Pole Coverage: This technique can provide better coverage for the upper pole of the breast, preventing a “bottom-heavy” appearance.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While subfascial placement offers advantages, it also carries potential risks:
- Animation Deformity: Contraction of the pectoral muscle can sometimes cause the implant to shift or appear distorted, a phenomenon known as animation deformity.
- More Complex Surgery: Subfascial placement is technically more challenging than subglandular placement, potentially requiring a longer surgical time and increased recovery period.
- Increased Post-Operative Pain: Placing the implant under the fascia can lead to more post-operative pain and discomfort, particularly during muscle movement.
- Potential for Implant Migration: In some cases, the implant may migrate or shift from its original position.
 Potential Implant Migration After Subfascial Placement
Potential Implant Migration After Subfascial Placement
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
Recovery after subfascial breast augmentation is generally longer than with subglandular placement. Patients can expect more pain and discomfort, especially during the first few weeks. Strenuous activities and lifting heavy objects should be avoided for several weeks. Following your surgeon’s post-operative care instructions is crucial for optimal healing and minimizing complications.
Ideal Candidates for Breast Implant Under Fascia
Subfascial placement is often recommended for women with:
- Thin breast tissue
- A history of capsular contracture
- Desire for a more natural look and feel
- Athletes or individuals who engage in regular strenuous activity
Choosing the Right Surgical Approach
The decision between subfascial and subglandular placement is individualized and should be made in consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon. Factors like anatomy, lifestyle, and desired aesthetic outcome will influence the best approach.
What is the difference between submuscular and subfascial placement?
Submuscular placement positions the implant entirely under the pectoral muscle, while subfascial places it beneath the fascia, partially covering the muscle. Subfascial placement offers a balance between the benefits of both subglandular and submuscular techniques.
How long does the recovery take for subfascial breast augmentation?
Recovery varies, but generally takes several weeks. Full recovery and return to normal activities may take several months.
Is subfascial placement more painful?
Generally, yes. Subfascial placement can involve more post-operative pain, especially during muscle movement, compared to subglandular placement.
“Subfascial placement allows for a more tailored approach to breast augmentation, providing a natural and aesthetically pleasing outcome for the right candidate,” says Dr. Emily Carter, MD, FACS, a board-certified plastic surgeon.
Conclusion
Breast implant under fascia offers a unique approach to breast augmentation with potential benefits for specific candidates. Understanding the advantages, disadvantages, and recovery process is crucial for making an informed decision. Consulting with a qualified plastic surgeon is essential to determine the most suitable surgical technique based on individual needs and goals. If you’re considering breast augmentation, discussing breast implant under fascia with your surgeon is a valuable step in achieving your desired aesthetic outcome.
FAQ
- What are the main advantages of subfascial breast implant placement?
- What are the potential risks of this procedure?
- Who is a good candidate for subfascial placement?
- How long is the recovery period?
- What should I expect during the recovery process?
- What is the difference between subfascial and subglandular placement?
- How do I choose the right surgical approach for me?
If you have further questions or require assistance, please don’t hesitate to contact us at [email protected] or visit our office at Fifth Avenue, 34th Floor, New York, NY 10118, USA. Our 24/7 customer service team is ready to assist you.
